
My Name Is Fester. It Means “To Rot.”
-
 Jared Dillian
Jared Dillian
- |
- May 25, 2017
- |
- Comments
But the old-timers know that when the cov-lite paper comes out, it is usually towards the end of a cycle.
Source: @tracyalloway
Let me define a few terms here, first.
When a company issues bonds, those bonds usually come with a legal agreement called an indenture.
The indenture has covenants which provide constraints on the borrower’s behavior over the duration of the loan.
There are no such restrictions on consumer debt. If you take out a car loan, and then you take out a bunch of student loans on top of it, there is not much the bank can do about it.
But in the world of corporate debt, you can. Bond covenants can take the form of restrictions on taking out additional debt, or maintenance of certain financial ratios, like interest coverage; stuff like that. If a borrower is found to be in violation of the covenants, the debt can be downgraded by a rating agency, or can be pushed into technical default.
Covenant-lite is when a company borrows from the public basically free of any restrictions whatsoever—kind of like your car loan. If they want to borrow from you, and then go and take out a bunch of additional debt, they can.
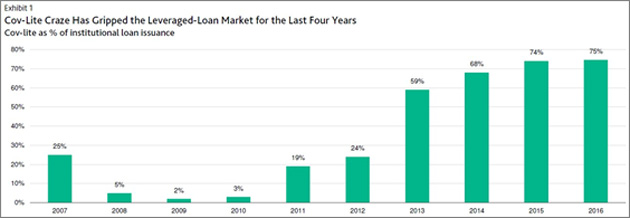
Here is how credit markets work. During bear markets, nobody trusts anybody, and bond indentures are full of covenants. In 2009, during the financial crisis, only 2% of bonds that year were considered to be covenant-lite.
Now, about 75% of bond deals are cov-lite, and it’s been that way for a while. At the top of the cycle, all the cov-lite deals come out. And bond investors are usually very sorry a few years later—when default rates rise, and recovery rates are far below where they would otherwise be.
PIK-toggle
The other thing that usually happens at the top of credit cycles is that the PIK-toggle bonds come out.
PIK stands for payment-in-kind. The borrower has the option of making its interest payments in cash…or more bonds!
This is very much like the negative amortization mortgages or option adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) that were going around during the housing bubble last decade.
I don’t currently have data on PIK issuance, but it’s definitely high.
All of this is when yields (and coupons) on debt are at historical lows, and people are taking on this immense additional risk just to get a 5% yield on very risky paper.
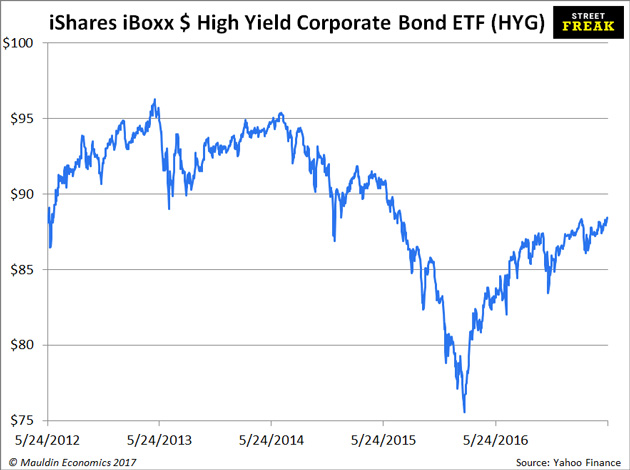
Here’s a chart of HYG, which is considered to be the benchmark high-yield ETF. It’s not a complete picture of the high-yield market, but it’s close enough.
The Default Rate
Like what you're reading?
Get this free newsletter in your inbox every Thursday! Read our privacy policy here.
During a recession, default rates can skyrocket to 10 or 12 or even 15 percent—annually. The cumulative probability that a given 5-year bond will default is very high. Yields get out to very high—and attractive levels.
I’ve had some success in timing credit cycles over my career. One of my greatest trades (even though it was small, because I was still young and poor) was to buy a high-yield convertible bond fund pretty much at the lows of the credit cycle in 2002. The yields were astounding. I like buying 14% bonds, not 5% bonds. Don’t you?
The Trade
What is the trade?
The trade is to evaluate your holdings of corporate debt, even the investment grade stuff.
A lot of investors have been pushed out the risk curve into high yield by low interest rates, and that’s not good. People have short memories about how exciting credit can get during a downturn. It’s even worse when you think about some of the possibility liquidity issues that the bond market could have in a disorderly market.
Lots of people think you have to short stuff to be a smart investor. Shorting is hard. I don’t like shorting stuff… Most of the time, just not buying it is good enough.
Cash is great. Keep your powder dry until the next downturn, get some of those 12-14% bonds.
It feels like I bring this up every other week—cash cash cash cash cash. Cash is an option to buy something at a lower price later. As the price of nearly everything is high right now, it’s a great time to hang out in cash.
One of the hardest things to do in investing is to wait—especially, to wait for an opportunity to come along. You feel like your money isn’t working for you. Yes, it’s a shame that there’s little-to-no interest in a bank account. That doesn’t mean you have to go out and take stupid risks just to make a couple hundred basis points.
Stepping off the soapbox now.
subscribers@mauldineconomics.com
Tags
Suggested Reading...
|
|

 Jared Dillian
Jared Dillian


